Signa SP / LOCALITE
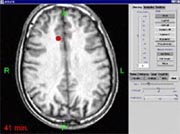
LOCALITE iMRI Navigator is an image-based navigation system for surgery using interventional magnetic resonance imaging (iMRI). The iMRI Navigator is being used in neurosurgery, in ENT subcranial surgery, orthopedic surgery and interventional radiology (minimally invasive liver surgery).
Components
Interventional magnetic resonance tomographs produce so-called realtime
images (slices) of the patient during the operation. The surgeon
determines the orientation of the slice in 3D space by changing
the position and orientation of his current instrument (pointer,
microscope, ...) that is optically tracked. The LOCALITE iMRI
navigation system works with open MRI systems that are specifically
designed for interventional use, but also with conventional, closed MRI
tomographs that have been retrofitted for intraoperative use. The iMRI
Navigator supports built-in devices, e.g. tracking camera and monitor;
our experts are happy to design and implement customized solutions,
such as beamers or separate tracking systems.
Planning
The
LOCALITE iMRI Navigator supports planning. Going well beyond
conventional navigation systems that work exclusively with
preoperative image data, the iMRI Navigator can update the plan during
the actual operation. Planning is essentially based on the data
from the interventional MRI tomograph. All other image data – planned
trajectories, images from various other systems, thermometry – are set
in relationship to the iMRI images. Realtime images in combination with
image data from the planning stage are particularly valuable to detect
and compensate for brainshift in neurosurgery.
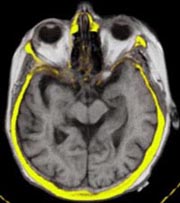
Co-registration and Fusion of Images
The LOCALITE iMRI Navigator can be used to co-register and merge images of
different modalities with the interventional MRI images.
CT:
Co-registration of CT and iMRI volumes may be marker-based or semi-automatic, using the
Mutual Information algorithm. Several different visualizations are
available for the merged volumes.
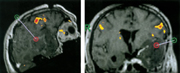
fMRI/PET:
Functional image data can be integrated just as well. In combination with the fMRI
volume, T1-weighted 3D functional data are acquired preoperatively.
They, too, can be co-registered with the
interventional images semi-automatically. Visualization is similar to that of CT data.
Online Imaging and Navigation
Based
on the planning for access or for more complex therapy (e.g.
thermotherapy), the surgeon can now use interventional image data for
navigation in two complementary ways. One way is to update the complete
MRI volume at intervals. The other way is to select a specific
slice, using the tracked instrument currently in his hand. This slice is
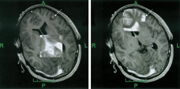
then scanned by the MRI. Major disadvantages of
using the realtime slice image are the time needed to perform the scan
(2 - 5 seconds) and the poor image quality, in particular from MRI with
low field intensity (.2 or .5 Tesla).
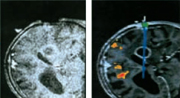
On the left, see a realtime slice (.5 Tesla) and, on the right, the
corresponding image from a preoperative volume (3D sequence, .5 Tesla).
The
LOCALITE iMRI Navigator lets the surgeon use specific vizualizations to
compare the realtime image and corresponding images from the planning
phase. When deviations are detected, the surgeon may acquire a current
iMRI volume and update the plan on its basis. This may be repeated as
necessary, leading to a process of iterative navigation.
For the surgeon these
options are not mutually exclusive but complementary:
The right picture above connects to the planning results, while the
realtime slice on the left lets him evaluate the residual 'goodness' of
the planning data that are no longer up-to-date.
Consulting, Research and Development
In many years of integrating various systems and technologies with
interventional MRI we have built a broad repertory of methodologies,
technologies and strong partners to assist you in planning navigation
applications for MRI and to design and implement a bespoke solution for
your requirements.